Aerodynamics is a study that determines vehicle aerodynamics. Aerodynamics actually represents the vehicle resistance to air at a given speed. When aerodynamic drag is optimised, it enables reduce energy consumption of the vehicle. But also, to improve its circulation by taking into account the outdoor conditions to the vehicle.
Aerodynamics have an impact on :
- L'Autonomy a vehicle
- Energy consumption (petrol, electricity, etc.)
- CO2 emissions
Aerodynamics is an important criterion in the design of electric vehicles. Especially when it comes to designing increasingly 'clean' vehicles. This is the reason behind 20% of energy consumption.
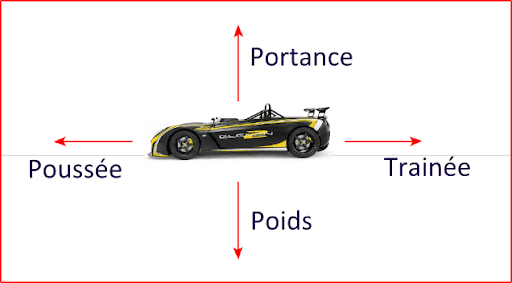
The main factors to be taken into account to improve the aerodynamics of the vehicle are - Lift, Thrust, Weight, Drag.
The coefficient used to calculate a vehicle's aerodynamics is :
How do aerodynamic optimisation tests work?
In the laboratory, the Volt is subjected to dynamic wind tunnel tests. A propeller produces a wind (~222 km/h) in the room, the effect of which on the vehicle is determined by a smoke that the engineers also emit. This smoke is used to study the action of the wind on the vehicleand therefore to rework the aerodynamic curves of the bodywork, and finally maximise air circulation on the walls of the vehicle.
Technical solutions to improve vehicle aerodynamics :
Active Spoiler | Aerodynamic Flaps | Active Wheels | Narrow Tyres | Lowering the vehicle's trim
Video -> Mercedes Benz Control Centre - Wind tunnel and aerodynamic test
What you need to know, aerodynamics is one of the factors the origin of aesthetics of the vehicle in question.
Similar articles :
- Test Drive Hyundai Ioniq Electric (38 kWh): the queen of efficiency
- Top 10: most powerful electric cars
- Test Drive Kia Niro EV 64 kWh: a spacious family car
Do you have any other questions?
« Toutes les définitions


