Everything you need to know about recharging electric cars: power and recharging time of charging points
Understanding the difference between AC and DC charging points
As the world turns to electromobility, the question of recharging becomes essential. Among the many technical terms, two stand out: AC and DC charging points.
But what do they mean and what are their differences?
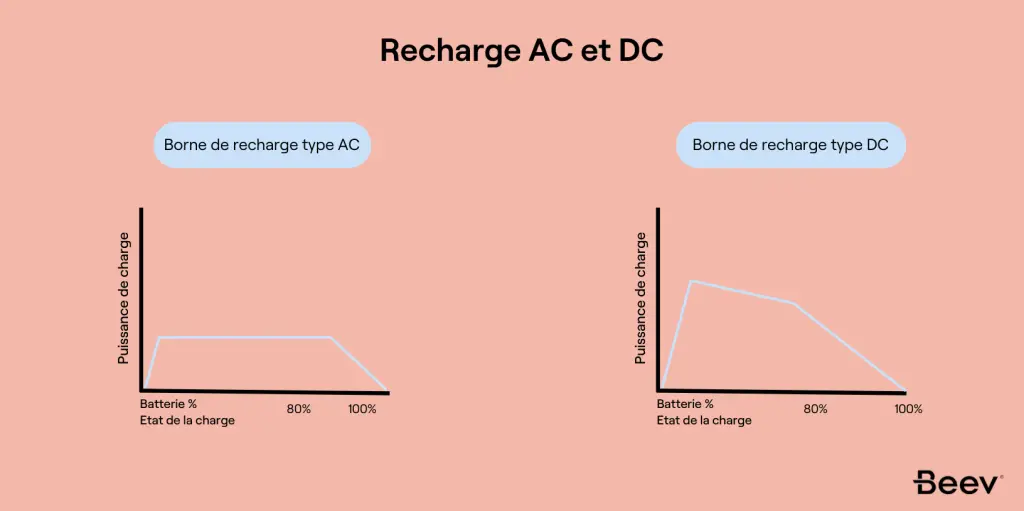
AC: Slow but regular recharging
AC charging points deliver an alternating current, similar to that of our wall sockets. This type of charging is slower than DC charging, with power ratings generally between 3.7 kW and 22 kW.
Benefits :
- Widespread : AC terminals are everywhere, in car parks, service stations and even at home.
- Cost-effective solution: They are generally cheaper to install and operate than DC terminals.
- Suitable for daily recharging : perfect for slow recharging at night or while parked.
Disadvantages :
- Longer recharge time : fully recharge a battery can take several hours.
- Limited power : is not suitable if you need to recharge quickly.
DC: Quick recharge, for those in a hurry
DC charging stations, on the other hand, supply a direct current that is directly compatible with the electric vehicle's battery. This technology allows ultra-fast chargingwith power ratings of up to several hundred kilowatts.
Benefits :
- Lightning refill : allows a large part of theautonomy in minimum time, ideal for long journeys.
- Perfect for occasional journeys: handy for quick recharging at a motorway stop.
Disadvantages :
- Less common : DC terminals are even less numerous than AC terminals.
- Higher cost : DC terminals are generally more expensive to install and use.
- Refill less suitable for daily use : Because of their high power, they are not ideal for slow recharging at night.
To sum up, what type of bollard should you choose?
The choice between an AC or DC charging point depends on your needs and your driving habits:
- if you are looking for a economical and practical daily recharging : opt for an AC terminal.
- if you need recharge your vehicle quickly on long journeys DC terminals are your ally.
To find out more, click here: Which electric recharging point should I choose?
Factors affecting the charging time of an electric car
Several factors influence the charging time of an electric car. Firstly, the capacity of the battery and the level of charge remaining have a direct impact on the time needed for a full charge. A larger capacity battery will logically take longer to fully charge.
The power of the charger used is also important. Slow domestic chargers (3-7 kW) can take several hours to fully charge, while fast-charging stations (50-350 kW) can recover 80% of range in around 20-40 minutes. Outside temperature also affects battery efficiency, slowing charging slightly in cold weather.
Finally, the condition of the battery and its ageing after several years of use can reduce its maximum charge capacity. Intelligent charge management, by modulating power according to need, optimises recharge times.
Read more: Impact of summer on electric batteries: what professionals need to know
Discover the different types of plugs and connectors for electric cars
Domestic sockets or public terminals: what's the choice?
Here is a summary of the main points to consider when choosing between a domestic socket or a public charging point to recharge your electric car:
Home recharging
The vast majority (around 80%) of electric vehicle owners opt for home charging, which is more practical and economical in the long term.
- Heavy-duty socket (3 - 7 kW): the least expensive solution (€60 - 130), but slower (full recharge in 8 - 12 hours). Suitable for short daily journeys.
- Wallbox / Domestic charging station (7 - 22 kW): faster (80% recharges in 2 - 4 hours) but the most expensive (€500 - €1,500 + electrical installation). Allows intelligent control and billing per kWh consumed.
It's a good idea to schedule charging during off-peak hours to reduce your electricity bill.
If you are interested ininstallation of a home charging pointDon't hesitate to contact us.
Public terminals
A minority use public charging points, a solution more suited to occasional use or as a complement to home use.
- Slow charging points (3-22 kW): free or chargeable (€0.36-0.72/kWh), sometimes with an annual subscription (€120 for individuals, €600 for professionals).
- Fast charging points (50-350 kW): for fast one-off recharges (80% in 20-40 min) on major roads.
Access often requires a subscription card, and charges vary from operator to operator (billing by kWh, charge, minute or session).
So, for everyday use, recharging at home with a reinforced socket or home terminal remains the most practical and economical solution, while public terminals are better suited to occasional use.
Public charging of an electric car: how does it work?
Finding and using public charging points
In France, finding a recharging point is easy thanks to more than 100,000 public charging points. Users can easily locate the nearest terminal to their current location using specialist mobile applications or dedicated websites.
These digital tools offer detailed information such as the location of the kiosks, the type of socket, the power available and, in some cases, the occupancy status in real time. To access these kiosks, you generally just need to register on a specific network or use an RFID card supplied by the service provider.
To find out more, click here: All the charging networks for electric cars, a comparison
Which electric recharging network is best for you in France?
| Network | Number of terminals | Types of terminal | Cover | Rates |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tesla | 4644 | Superchargers (up to 250 kW) | Mainly along motorways | 0.36 €/kWh |
| Ionity | 1700 | Fast charging stations (up to 350 kW) | Motorways and trunk roads | 0.79 €/kWh |
| TotalEnergies | 1073 | Fast and normal recharging points | National coverage | 0.52 €/kWh (up to 50 kW) |
| Fastned | 300 | Fast charging stations (up to 350 kW) | Mainly along motorways | 0.59 €/kWh |
| Izivia | 8000 | Normal and accelerated charging points | National coverage | 0.40 €/kWh (up to 22 kW) |
| Allego | 15 000+ | Fast and normal recharging points | Europe, including 3,000 in France | From €0.30/kWh |
| Alizé | 3 000+ | Normal and accelerated charging points | France | From €0.25/kWh |
| Driveco | 2 000+ | Fast and normal recharging points | France | From €0.30/kWh |
| EVzen | 1 500+ | Fast and normal recharging points | France | From €0.40/kWh |
| Freshmile | 1 000+ | Fast and normal recharging points | France | From €0.35/kWh |
| KiWhi Pass | 1 000+ | Fast and normal recharging points | France | From €0.29/kWh |
Payment by bank card mandatory for charging stations: the electric charging revolution is underway

13 April 2024 is a key date for electric car charging in Europe. New regulations and initiatives are being put in place to encourage the uptake of electric vehicles and improve the energy efficiency of vehicles.recharging infrastructure.
From now on, all new fast-charging stations, with a minimum capacity of 50 kW, will have to display the cost of charging in euros per kilowatt-hour (€/kWh), adopting a model similar to the pricing of conventional fuels per litre.
In addition to this requirement for transparent pricing, electric vehicle users will need to have real-time access to information on prices and the availability of recharging points via digital channels.
This greater transparency will enable electric vehicle owners to better manage their costs and plan their recharges more efficiently. What's more, these new recharging stations will have to accept payment by bank card at no extra charge, unlike the current practice of using dedicated recharging cards or specific applications for electric vehicles.
NB: These regulations only apply to new fast-charging stations. Existing installations have until 2027 to comply with these standards.
Charging your electric car at home: how does the installation work?
Installing a Wallbox at home: how and for how much?
Here you'll find the main information on installing a Wallbox (electric vehicle charging point) at home and its cost.
How do I install a Wallbox at home?
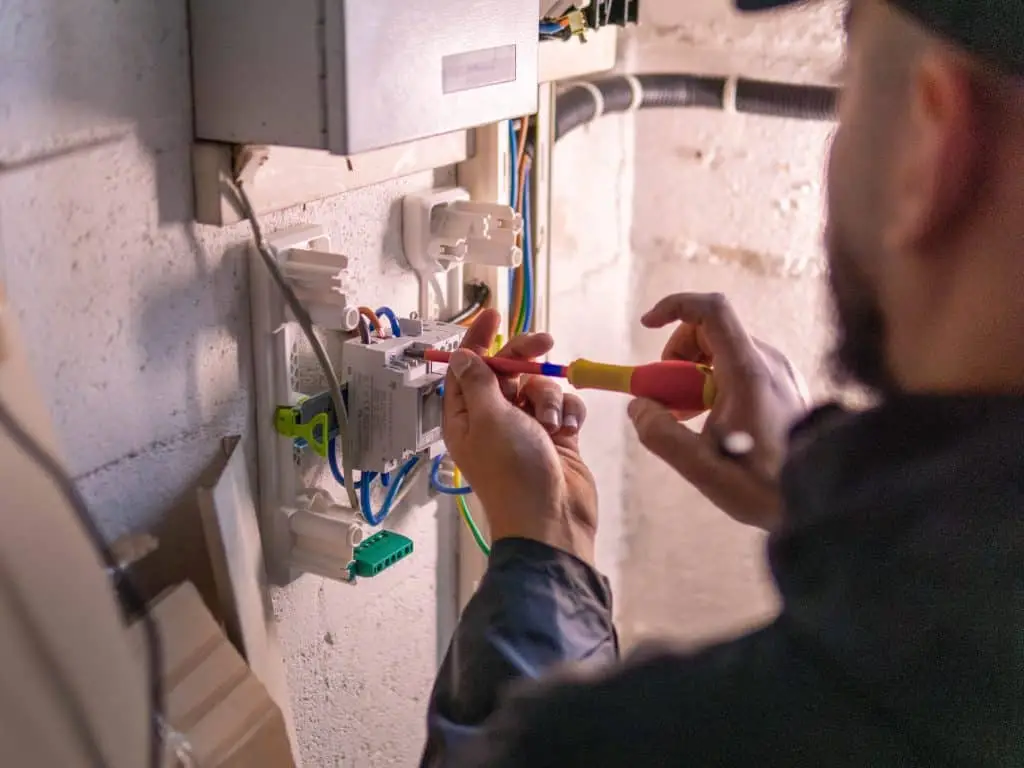
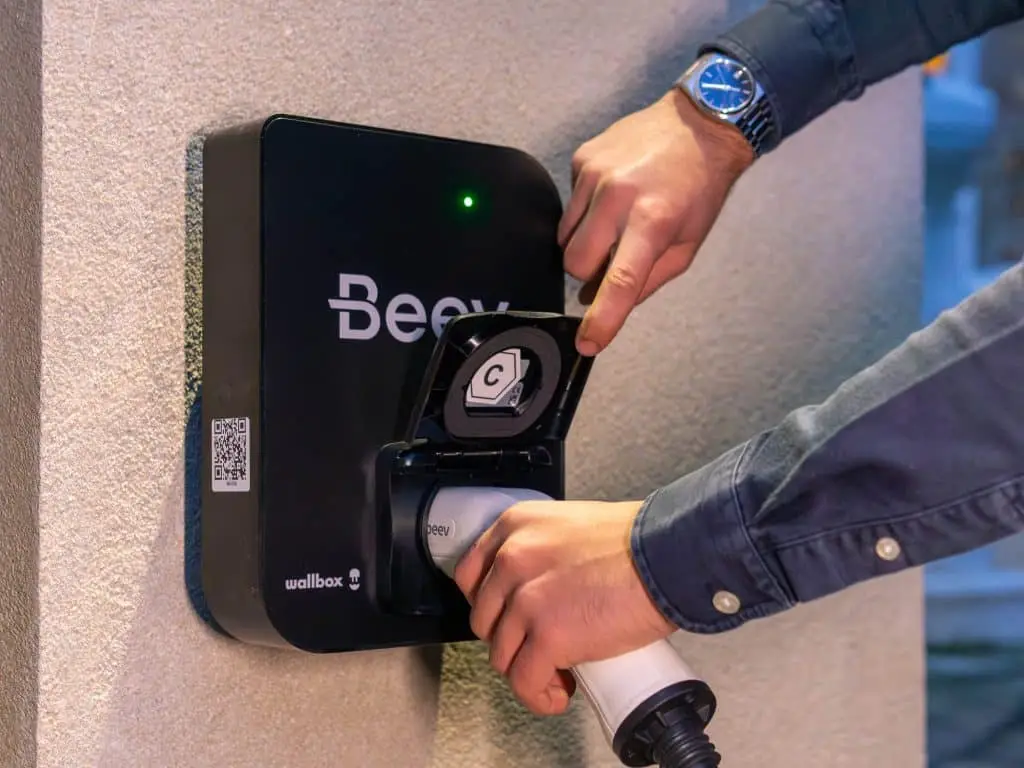




Installation must be carried out by an IRVE-certified professional electrician, and not self-installation, for safety and warranty reasons. In some countries, such as France, self-installation is even illegal.
The process usually includes the electrical connection of the Wallbox, possibly with an upgrade of the existing electrical circuit, as well as the laying of an RJ45 network cable for connectivity.
A power management unit (Power Boost) can be added to optimise charging according to the home's consumption.
Wallbox installation costs
The cost varies according to the brand, the Wallbox model (3-22kW), the distance of the electrical connection and any work required to upgrade the circuit.
For a basic Wallbox, allow around €500-1500 for purchase and installation by a professional. Top-of-the-range models can cost more than €2,000 to install. The Power Boost represents an additional cost of around €300-500, depending on the model.
Professional installation costs are generally included in the sale price, but it is advisable to check carefully and ask for a detailed quote.
So for a complete turnkey installation of a high-quality domestic Wallbox with intelligent management, you need to budget between €800 and €2,500, depending on the options you choose.
Read more: Wallbox Pulsar Socket vs Easee: which terminal to choose?
Financial aid for home installation of a charging point 2024
The government has introduced a number of financial aid to encourage the transition to electric mobility. These include :
- a tax credit of €500 per controllable recharging point for individuals living in single-family homes
- VAT reduced to 5.5 %.
Tax credit
The newly introduced tax credit, which replaces the CITE (tax credit for energy transition), means you can now claim a tax deduction of €500 for each controllable charging point installed in your home.
To qualify, a number of criteria must be met, including the installation of a controllable charging system, defined as a device capable of modulating the power demand or programming the recharging of the electric vehicle. What's more, you need to use a professional qualified in electric vehicle charging infrastructure.
The amount of the tax credit is calculated at 75 % of the expenditure incurred for the acquisition and installation of the equipment, with a ceiling of €500 per charging point for the 2024 financial year. This amount was previously set at €300 per charging point until the end of 2023, with no requirement for a controllable charging point.
In practice, for a couple subject to joint taxation, the installation of two home electric charging points can give entitlement to a tax credit of 2 x €500. If the amount of tax due is less than the amount of the credit, the tax authorities will refund the difference.
We strongly recommend that you keep a detailed invoice for the work carried out, giving details of where the work was carried out, the technical description of the charging point and the total cost incurred. Although the invoice is not required for tax purposes, it is essential that you keep it in case the tax authorities carry out any checks.
NB: Unfortunately, opting for a reinforced Green'Up (Legrand) type plug will not entitle you to a tax credit, unlike installing a charging point.
Reduced-rate VAT
Since the beginning of 2021, an advantageous tax measure has been in place for private individuals: reduced-rate VAT is now applicable to work on the installation, fitting and maintenance of charging systems, provided it is carried out by a qualified professional, in particular an electrician specialising in Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure (IRVE). This requirement is now a legal obligation for charging points with a power rating of 3.7 kW or more.
This measure applies to various categories, including owner-occupiers, landlords, co-owners' associations, tenants and free occupiers. However, professionals and legal entities are not eligible.
From 1 January 2023, a major administrative simplification will be introduced: it will no longer be necessary to provide the installer with proof that the property is old. The date of construction of the home will no longer be a determining factor in qualifying for the reduced rate, which will greatly simplify the process for potential beneficiaries.
Financial aid for the installation of a charging point for professionals 2024
Advenir bonus for companies
Under the Advenir programme, the amount of aid granted is determined according to the composition of the family. vehicle fleetwhich may include light or heavy vehicles, and the connection capacity of the project infrastructure, which may be less than or greater than 500 kVA.
For the installation of charging points in a private car park open to the public, the Advenir premium can cover up to 30 % of the cost (excluding tax) of supplies, equipment and works, with a limit of €1,000 to €2,700 (excluding tax) per charging point.
For the installation of recharging points in car parks dedicated to company fleets and employees, the Advenir bonus can be up to 20 % of the cost (excluding tax) of supplies, equipment and works, with a limit of €600 per recharging point.
To find out more, click here: What changes will there be in 2024 to support for the installation of terminals in businesses?
Charging your electric car: advice to follow
Limit recharging of your electric car to 80%
It is generally recommended not to charge your electric car to 100 % and to limit charging to 80 % for several reasons. Firstly, this helps to preserve the battery's lifespan. Each charge and discharge cycle wears down the battery, and the more the battery is charged to 100 %, the greater the number of full charge cycles, which can reduce its lifespan. By limiting the charge to 80 %, the number of full charge cycles is reduced and the life of the battery is extended.
Secondly, it reduces charging time. The charging speed of a battery is highest when it is lightly charged, and decreases as the battery fills up. So the last 20 per cent of the charge can take as long as the first 80 per cent. Limiting the charge to 80 % therefore reduces the total charge time.
Lastly, this can help to reduce charging costs, particularly at fast-charging stations. Some charging points charge according to the charging time, not the amount of electricity consumed. Limiting charging to 80 % reduces charging time and therefore the cost of charging.
However, these recommendations may vary depending on the type of battery, the make and model of electric car, and the conditions of use. It is therefore important to refer to the manufacturer's instructions and to consult a professional if in doubt.
See how long it takes to recharge your electric car
The charging time for an electric car depends on a number of factors, including the battery capacity, the initial charge level, the maximum charging power of the car and the charger used, and the weather conditions.
A full charge from a standard household socket (230V, 16A) generally takes between 8 and 12 hours for an electric car with a 40 kWh battery, and between 12 and 18 hours for a 60 kWh battery. However, charging speed can be much faster at a public charging point or a home wallbox.
A 40 kWh battery can be recharged to 80 % in around 30 to 40 minutes at a fast charge point (DC) with a maximum charging power of 50 kW, and a 60 kWh battery in around 45 to 60 minutes. At an accelerated charging point (AC) with a maximum charging power of 22 kW, it takes around 2 to 3 hours to recharge a 40 kWh battery to 80 %, and around 3 to 4 hours for a 60 kWh battery.
Use a suitable recharging point
Make sure you use a charging point that is compatible with your electric car. Charging points may have different connectors and charging powers.
Plan your journeys
Before you set off, check the range of your electric car and plan your recharging stops if necessary. A number of applications and websites can help you find the charging points available on your route
Conclusion
The future of electric vehicle charging looks bright, with constantly improving infrastructure, increasingly efficient charging technologies and a collective awareness of the importance of environmental sustainability. Electric charging is no longer a constraint, but an integrated part of the modern driving experience, demonstrating a commitment to a greener future.
If you're thinking of installing a charging point for business or at home, our Beev experts are on hand to advise and support you in your project. Don't hesitate to contact us.




































