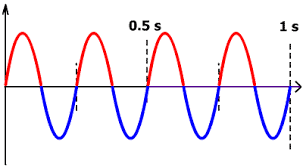
Alternating current (AC) is a type of electric current whose electrons flow from periodically. It comes in the form of cycles and changes direction twice per period. The chemical activity of a generator produces this current, which powers the battery then the engine.
This type of current team most of the batteries in current electric vehicles.
- Why is this type of current more popular than its cousin, direct current (DC)? ?
Alternating current (AC) is much more favourable for transmission. It minimises energy losses. Its capacity is more than sufficient and optimal for charging an electric vehicle when used as is. For this reason, this type of current is most often installed in household sockets. But it can also be used for anything that requires recharging on a daily basis.
This is the case for any kind of energy transmission or distribution. These may include household appliances, digital equipment, etc.
In the case of electric vehicles, this alternating current is stored and then converted using a current variator. The most powerful transforms then in direct current, and sends the energy to the motor.
In Europe, this current is 50 cycles per second, i.e. a frequency of 50 Hz.
Similar articles :
- How much recharging power do you need for your electric car?
- Hotel with charging point: A must-have
- Video - How much recharging power do you need for your electric car?
Do you have any other questions?
« Toutes les définitions