Use the TCO simulator to calculate the total cost of ownership of your car and compare it with its internal combustion equivalent.
Earthing: what does it mean?
In electricity, earthing, also called earthing or MALTis an essential safety system that protects people and property against the dangers of leakage current. The principle is simple: connect the metal parts of electrical appliances and the building's grounds to a ground spikeThis is to evacuate deviating currents towards the ground in the event of an insulation fault.
Imagine an electrical appliance with a damaged wire, exposing the live metal part. Without earthing, touching this appliance could result in electrocution. On the other hand, with an effective earthing system, the leakage current will flow to the ground via the earth wire, tripping the circuit breaker and cutting off the current, thus protecting you from danger.
Earthing is mandatory in all electrical installations comply with current safety standards, such as NF C 15-100 in France. It plays an essential role in preventing electricity-related accidents in the home, and is indispensable for guaranteeing the safety of the occupants of a home or building.
Read more: Do I have to change my electricity contract when I install a charging point?
Earthing and bonding: what's the difference?
Earthing and bonding are two related but distinct concepts in electricity.
Earthing is a global process that consists of connecting all the conductive elements of an electrical installation to earth potential, thus ensuring the safety and correct operation of the system. It encompasses all the connections and devices needed to create this link with the ground.
The earthing point, on the other hand, is a specific and physical element of this system: it is the actual point of contact with the ground, usually in the form of a metal rod driven into the earth or another conductive device in direct contact with the ground. In other words, the earthing system is an essential component of earthing, but is only part of the overall process.
Earthing includes not only the earth connection, but also all the conductors, connections and devices that link the various elements of the electrical installation to this earth connection.
What does NF C 15-100 say about earthing?
La NF C 15-100 standardwhich governs low-voltage electrical installations in France, sets out precise earthing requirements to ensure the safety of people and property. Here are some key points to remember:
Obligatory earthing
According to the standard, it is compulsory to earth all metal parts of electrical installations, including pipes, frames and other metal components.
Earth connection
The standard specifies that the earthing system must consist of a set of conductors and electrodes buried in the ground, guaranteeing an earth resistance below the maximum authorised value, depending on the type of earth leakage circuit breaker used.
Equipotential bonding
According to the standard, equipotential bonding is required to connect the various metallic masses in the installation, thereby standardising their electrical potential and improving protection against electric shock.
Protective conductors
The standard defines the characteristics of the protective conductors, the green-yellow coloured wires that connect the metallic grounds to the earth connection.
Checks and maintenance
The standard requires periodic checks to be carried out on earthing and equipotential bonding to ensure that they function properly and are effective over the long term.
Compliance with the requirements of standard NF C 15-100 is essential to guarantee the safety of electrical installations and to protect people from the risks associated with leakage currents. It is therefore essential to have earthing work and periodic inspections carried out by a qualified electrician.
How can I check whether a home is correctly earthed?
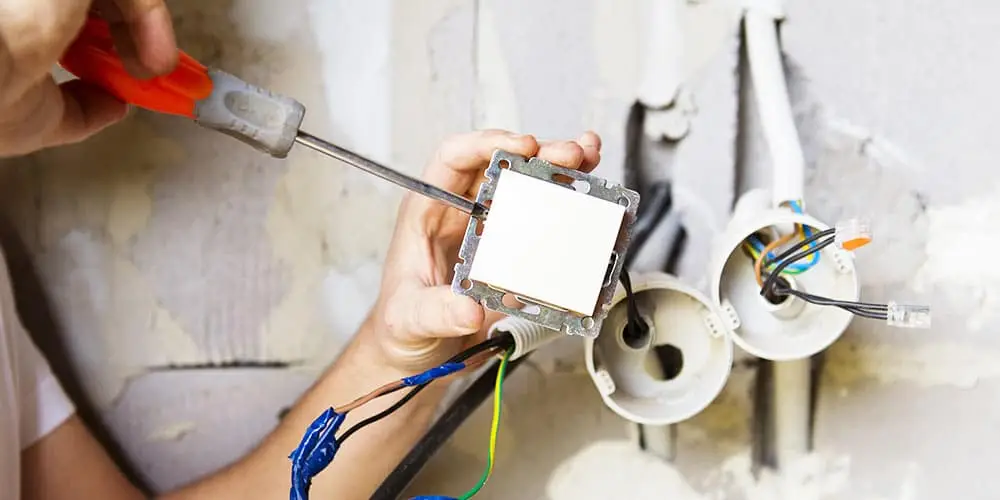

Checking that your home is properly earthed is an important step in ensuring the electrical safety of your home. To make sure your home is properly earthed, start by visually inspecting the main electrical panel to locate the earth wire, which is usually green and yellow. Then use a socket tester to check that each socket is properly earthed. If you have any doubts, call in a qualified electrician who can carry out more thorough tests, such as measuring the earth resistance using an ohmmeter.
It is important to note that checking the earthing system should not be neglected, as incorrect earthing can lead to the risk of electric shock or fire.
If a problem is detected, don't hesitate to call in a professional to carry out the necessary work and ensure that your electrical installation complies with current standards.
What equipment needs to be earthed?
To ensure everyone's safety, the following elements must be earthed:
- Your home's electrical panel, which must be fitted with an earth bar and an earth terminal block (green in colour).
- The electrical circuits in your home, and by extension, all sockets used to connect Class I appliances, identified by the ⏚ symbol (such as electric radiators and household appliances).
- VDI (voice, data and image) network ducts, including the communication box, if you have one.
- The main equipotential bonding points in the home, i.e. points containing metal parts that are likely to be conductive (such as metal door or window frames, pipes, etc.).
- Equipotential bonding in shower rooms, in accordance with standard NF C 15-100, particularly in bathrooms.
Earth connection: how much does it cost?
The cost of an earth connection varies according to a number of factors, such as :
Type of accommodation
Single-family homes are generally more expensive to earth than flats, as the length of the cables and the complexity of the work can be greater.
The condition of the electrical installation
If the existing electrical installation is old or in poor condition, additional work may be required, which will increase the price.
The chosen earthing technique
There are various grounding techniques, and their cost can vary. The most common technique is to install an earth spike in the ground, but there are other solutions, such as earthing via the water distribution network or a reinforced concrete foundation.
Accessibility of the site
If the site is difficult to access, this can also increase the cost of the work.
As a general rule The cost of an earth connection is between 300 and 1,000 euros (including tax).
Here are some examples of prices:
- For a flat: between 300 and 500 euros including tax
- For a single-family home: between €500 and €1,000 including VAT
It's important to get quotes from several electricians before carrying out the work.
How do you install soil in a house?
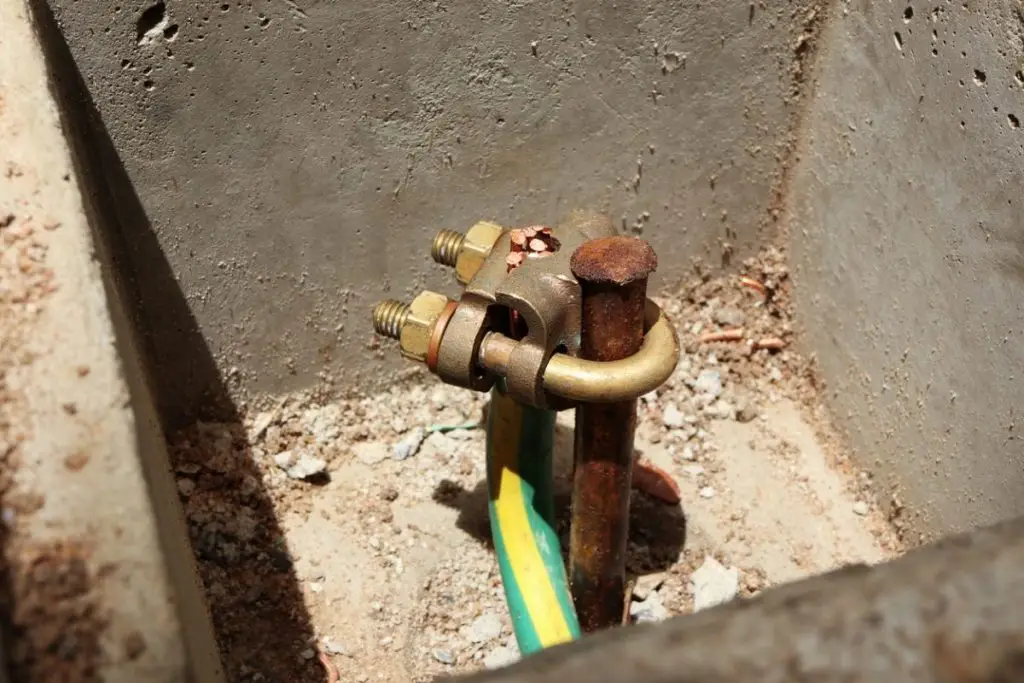

Down-the-hole loop: earthing integrated into the building's foundations
The down-the-hole loop is an effective and economical method of earthing a house, integrated directly into the building's foundations. This technique involves installing a bare copper conductor in the foundation trenches, forming a closed loop around the structure.
This system has several advantages: it offers excellent electrical conductivity thanks to direct contact with the ground, it is protected from mechanical damage and corrosion by the concrete of the foundations, and it allows the fault current to be distributed evenly around the building.
What's more, this method simplifies the construction process by integrating earthing from the earliest stages of the worksite, reducing costs and installation time compared with other techniques. The trenchless loop is therefore the preferred solution for ensuring optimum electrical protection while complying with current safety standards.
Earthing rods: the ideal earthing solution for electrical renovations
The earth spike is an ideal solution for earthing during electrical renovation, and is particularly suitable for older homes. This method involves driving a metal rod into the ground, creating a reliable connection to earth to carry away fault currents. This method is often preferred for renovations, as it does not require major work such as that required for an underground loop, which has to be installed before the building foundations are laid.
To install an earth stake, we recommend choosing an accessible location, such as a cellar or a space under a concrete slab. The post should be sunk to a depth of at least one metre to ensure good conductivity.
Once the pole is in place, it is connected to the electrical panel via a copper earth conductor, often with a cross-section of 25 mm², and a breaker strip to isolate the indoor installation from the outdoor one.
This method ensures that the electrical installation complies with standard NF C 15-100, protecting occupants from the risk of electrocution and electrical appliances from damage caused by leakage currents.
How is an electric vehicle charging point installed?
Conclusion
In conclusion, earthing is essential for electrical safety, evacuating leakage currents and preventing the risks of electrocution and fire. Compulsory under standard NF C 15-100 in France, it includes the earthing system, equipotential bonding and protective conductors.
To check and maintain effective earthing, regular inspections by qualified professionals are essential. Costs vary between €300 and €1,000, but this is an important investment to ensure the safety of electrical installations and the protection of occupants.
If you would like to find out more about the tax credit for in-car charging points 2024For more information, see our article on this subject.
Would you like to install a recharging point?
Beev can help you find the charging point and installer you need, at the best price.
































