Our experts answer your questions with a smile
Monday to Friday 9am - 12.30pm - 2pm - 7pm
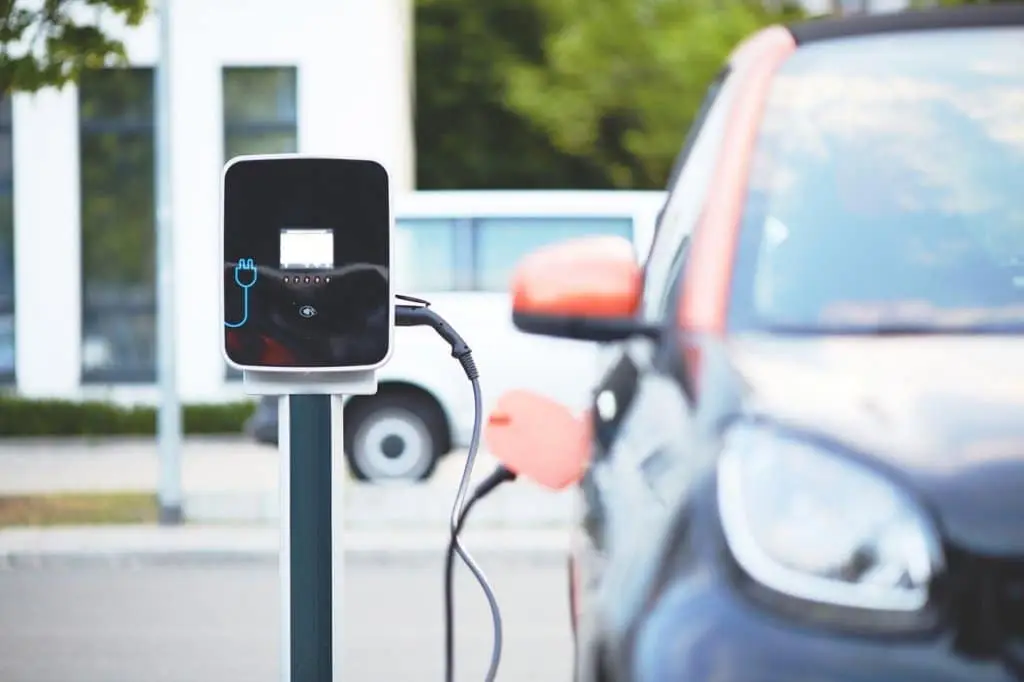
What are the different types of socket for recharging electric vehicles?
Home recharging, the simplest solution
According to Avere, thehe majority of recharge at home or at workThe rest is done at public charging points. Most recharging of your electric vehicle will therefore take place at home. There are two options:
- Use a standard household socket with the charging cable supplied with your vehicle. (approximately 10 to 15 kmautonomy recharged per hour)
- Have a charging point in the form of wallbox or reinforced grip. For example, the Green'Up Access is a domestic socket designed for recharging electric vehicles (approximately 20 to 40 km of recharged range per hour).

The wallbox
The wallbox is the most recommended to recharge your electric vehicle. This is a charging point for electric vehicles designed for domestic use. Its dedicated power line will ensure faster, smarter recharging.
The domestic socket was not designed for recharging electric vehicles. The wallbox, on the other hand, has been designed to support the power needed to recharge regular and fast electric vehicles. So you can recharge more than twice as fast using a wallbox.
The wallbox can also adapt to your electricity network. For example, in the event of peak consumption, typically in the morning. When you turn on the television, coffee maker and toaster at the same time, the wallbox can adapt the vehicle's charging power to avoid tripping the electricity meter.
This is called load shedding. A wallbox can also be configured to charge the electric vehicle during off-peak hours, saving you money.
So it's with peace of mind that you plug in your vehicle at home in the evening and know that it will be recharged to 100 % the next morning for your day.
Charging at public charging points, a network that is being rolled out and high charging speed
There are two main categories of terminals:
- The terminals to which the cable is attached
- The charging points to bring your charging cable to
According to a study sponsored bythe Direction générale des entreprises (DGE), du climat (DGEC), and Ademe, entitled "Analyse : Infrastructures de recharge pour véhicule électrique" (Analysis: Electric vehicle charging infrastructure). charging stations are still very uneven and inadequate in France. However, the situation is improving with the government's determination to develop this sector and the arrival of new players on the market such as Fastned and IONITY.
There are 3 main types of socket on public terminals:
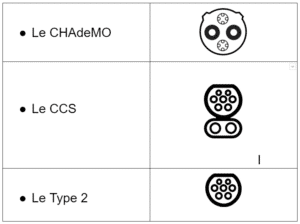
In Europe since 2017, a directive (2014/94/EU) stipulates that all fast-charging stations must be equipped with the CCS standard. This is the standard that has been chosen for the future of fast charging in Europe. This is something to bear in mind when reselling your future electric vehicle, as it will affect its residual value.
Although until 2024In France, the majority of fast-charging stations are equipped with all three standards. It is estimated that CCS will become the prevailing standard in the next few years.
From networks such as IONITY have already opted out of the CHAdeMO, to deploy terminals equipped only with CCS.
What are the different ways of recharging an electric vehicle?
Connecting the vehicle to the electricity grid
When we talk about recharging methods, we need to understand how the electric vehicle is connected to the electricity grid and how the electric current reaches the vehicle.
Le electric current exists in two different forms,
- Alternating current (AC)
- Direct current (DC)
To put it simply, AC current is found in the electrical sockets in the home, and DC current in the batteries, so it is transformed, which affects the speed of recharging.
Le alternating current (AC) and direct current (DC)
Now for a little explanation:
Alternating current (AC) is easily transported over long distances and is perfect for domestic use. In your home, the current that reaches the sockets is alternating current.
Direct current (DC) is used to store energy in batteries. It powers all your devices, from your smartphone to your electric toothbrush.
For transform AC current into DC current using a rectifier (or AC/DC converter)We'll simply call it a charger. All electric vehicles are equipped with a charger to transform AC current from the grid into DC current stored in the battery. battery.
However, the more powerful the charger, the heavier and more expensive it is. These are characteristics that do not lend themselves to use in an electric vehicle. Hence the interest of charging stations These are powerful chargers that recharge your electric vehicle very quickly.
When using a charging point fast, the current is not transformed in the vehicle, but in the terminal, then injected directly into the battery.
With fast charging, you can recover several hundred kilometres of range in just a few minutes, opening the door to long-distance journeys.
The 4 charging modes
There are 4 charging methods for electric vehicles. We have summarised how they work in these infographics. In all cases, when the electric vehicle is charging, the charging cable is locked into the vehicle's socket.
It is impossible to start it while it is still plugged in. The recharging mode defines how your vehicle is connected to the electricity network for recharging, and will determine the speed at which your batteries recharge.
We will not deal with mode 1 because it is obsolete today and does not meet electrical standards. An electric vehicle compatible with mode 4 will be compatible with mode 3, which will be compatible with mode 2.
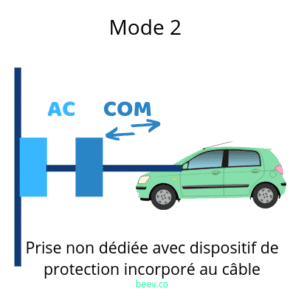
Mode 2 (standard AC load)
Mode 2 involves plugging into a conventional household socket, as you would plug in your smartphone in the evening. The charging cable used has a system for regulating the charge. In other words that this device ensures the safety of the connection by communicating with the electric vehicle and protects the user from electrocution.
All electric vehicles are now supplied with a cable of this type when the vehicle is purchased.. Use a reinforced electrical socket such as the Green'Up Access allows you to recharge your electric vehicle twice as fast.
Mode 3 (intelligent AC charging)
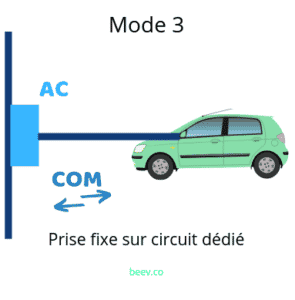
Mode 3 is characterised by the use of a dedicated electrical circuit, i.e. an electrical line directly connected to the electricity meter. This is to avoid wear and tear on the home's electrical network in the event of regular charging. An installation of this type is recommendedIt offers a number of advantages over mode 2.
Unlike mode 2, mode 3 enables intelligent charging of the vehicle. Typically a wallbox or charging point allows power to be regulated during charging to adapt to the constraints of the grid. In other words, the power adapts to the amount of energy available in the house in real time.
So there's no risk of a power cut while the electric vehicle is charging. This type of installation is very interesting because it also allows you to optimise your charging to take advantage of off-peak rates and save money on your charge.
READ ALSO - When should you recharge your electric car?
A wallbox installation is an investment that needs to be factored into the cost of buying an electric vehicle. However, as with the eco-bonus, there is state aid linked to the installation of a wallbox. charging point. This means that a specific installation costs around €500 if it is not supplied with the vehicle.
READ ALSO - Electric vehicle charging points in condominiums: the complete guide
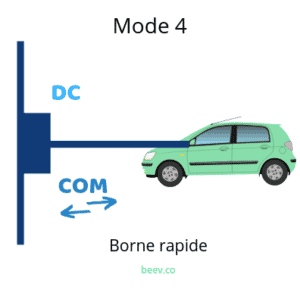
Mode 4 (DC fast charge)
Mode 4 is defined by a direct current (DC) load. Better known as "fast charging'. DC charging recovers 80 % of its range in less than 30 minutes. The exact recharging time depends on the vehicle and the battery temperature (if extreme). Fast-charging stations are generally located in motorway service areas and large conurbations. Several networks are being developed, such as those ofIziva,IONITYand Fastned
READ ALSO - How do you recharge your electric car on the motorway?
The different plugs for recharging your electric vehicle, summary table
What are the latest requirements for Recharge standards?
With the rapid development of electric vehicles, charging standards need to be regularly updated to ensure the efficiency and safety of the infrastructure. In 2024, several significant changes have been introduced:
- Charging stations must now be compatible with different networks to enable users to charge their vehicles without restriction, regardless of the supplier..
- Newly installed charging stations must have a minimum output of 22 kW for Type 2 connectors and allow high-power charging for Combo2 connectors.
- Operators must ensure the ongoing maintenance of the charging points and guarantee that charging continues even if communication between the charging point and the supervision centre is lost.
- The terminals must comply with strict safety standards, including devices to prevent overvoltage and guarantee the integrity of the load.
If you would like to find out more aboutsupport for the installation of charging points for private customers in 2024For more information, see our article on this subject.
































