Monday to Friday
9am - 12.30pm - 2pm - 7pm
What are mileage allowances?
Kilometric allowances are financial compensation paid by the company to a company employee who uses his or her personal vehicle for business purposes.
It is important to distinguish between a company car and a company vehicle, which, as the name suggests, is owned by the company and made available to an individual in the course of his or her duties.
The mileage allowances therefore relate to a personal vehicle that does not belong to the company.
This financial compensation takes into account various factors:
- Fuel costs
- Wear and tear on the vehicle
- Vehicle depreciation
- Repair and maintenance costs
- Insurance premiums
This financial compensation does not take into account :
- interest on loans taken out to purchase the vehicle
- vehicle parking charges (car park hire or parking meters)
- motorway tolls
- unforeseen expenses (repairs, accidents, etc.) unless the accident occurred during the business trip.
The flat-rate mileage scale can now be used whether or not you own the vehicle used. If, for example, someone in your tax household owns the vehicle, you can use the flat-rate mileage scheme.
Calculate mileage allowances 2024
Kilometric allowances are calculated on the basis of two parameters:
- the fiscal power of the vehicle registration document (section P.6 of the vehicle registration document)
- the mileage over the calendar year
To calculate your mileage allowance, go to the simulator by clicking here.
The calculation process for mileage allowances in 2024 for electric cars is simple and involves two main stages:
- Apply the standard mileage rate The first step is to apply the standard mileage scale, which takes into account the tax rating of your vehicle and the distance travelled for business purposes.
- Add the 20% surcharge Once the amount has been calculated, add a surcharge of 20% to reflect the use of an electric vehicle.
Example: suppose you own a 4 HP electric car that has travelled 6,000 km for business purposes. The calculation would be: [(6,000 x 0.340) + 1,330] x 1.20 = €4,044.
This amount represents what you can deduct from your income as deductible mileage expenses for the year.
What costs are covered?
The kilometric scale covers the following elements on a flat-rate basis:
- Vehicle depreciation
- Repair and maintenance costs
- Tyre wear
- Electricity consumption for recharging
- Insurance premiums
Please note! Loan interest, parking charges and tolls are not included in the scale, but may be added to the amount calculated if they can be justified.
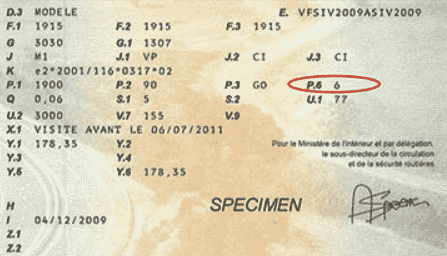
The calculation of mileage allowances follows a scale set up by the tax authorities.
| Puissance fiscale | Jusqu'à 5 000 km | De 5001 à 20 000 km | Plus de 20 000 km |
|---|---|---|---|
|
3 CV and less
|
d * 0.529 * 1.20
|
(d * 0.316) + 1065 * 1.20
|
d * 0.370 * 1.20
|
|
4 CV
|
d * 0.606 * 1.20
|
(d * 0.340) + 1330 * 1.20
|
d * 0.407 * 1.20
|
|
5 CV
|
d * 0.636 * 1.20
|
(d * 0.357) + 1395 * 1.20
|
d * 0.427 * 1.20
|
|
6 CV
|
d * 0.665 * 1.20
|
(d * 0.374) + 1457 * 1.20
|
d * 0.447 * 1.20
|
|
7 CV and more
|
d * 0.697 * 1.20
|
(d * 0.394) + 1515 * 1.20
|
d * 0.470 * 1.20
|
d = distance travelled in km during the year.
Good to know: the rate per kilometre has increased by 5.4% in 2024. This increase takes account of inflation and the rise in fuel prices for business travel.
Kilometric allowances and income tax
Kilometric allowance allows employees to deduct business expenses on his income tax return. These business expenses include commuting costs.
This is a tax advantage for employees who are obliged to use their private vehicle in the course of their work.
There are two types of deduction for income tax purposes:
- flat-rate deduction
- deduction of actual expenses
Flat-rate deduction
This is a flat-rate deduction of 10 % which is automatically calculated from your salary to take account of your travel expenses.
There are ceilings:
- The deduction is at least €495 for each member of the tax household, compared with €437 in 2023.
- The maximum is €14,171, compared with €12,502 in 2023 for each member of the household.
The previous simulator is not useful, as it is calculated directly from your salary.
Deduction of actual expenses
When you do your calculations, if you think that the flat-rate deduction does not cover your expenses, you have the choice of opting for the actual deduction of your expenses.
To be eligible, your mileage expenses must be:
- justified you must keep all documents and invoices attesting to the actual amounts spent
- paid during 2019
To calculate the exact amount, refer to the scale in the previous section.
Declaring your income tax
Flat-rate deduction
In the case of the flat-rate deduction, the authorities automatically apply the flat-rate deduction of 10% to your wages, so you don't need to do anything.
Deduction of actual expenses
If you wish to deduct actual expenses, you must :
- Indicate the amount of mileage expenses you are claiming as a deduction
- Itemise your actual expenses in an attached note, specifying their nature and amount.
- All supporting documents (invoices) must be kept for a period of 3 years.
Mileage costs for an electric car
For electric vehicles, the rental of the battery and the cost of recharging it is taken into account under fuel costs and is therefore already included in the scale.
In other words, as this scale has been calculated for internal combustion vehicles that consume fuel, you will have a significant advantage with this calculation.
Example
I own a 3 hp electric car that I use for my 60 km daily commute to and from work.
I work 200 days a year, so I drive my car 12,000 km a year in the course of my work.
Given that recharging an electric vehicle is much cheaper (€2/100km), that's €240.
Mileage allowance = (d x 0.3) + 1007
= (12 000 x 0,3) + 1007
= 4 607 €
This is a considerable advantage for electric car drivers, given the very low horsepower and low fuel consumption of these vehicles.
For more information, we've put together a guide to this topic to explore the different aspects in depth:
Read our article about :