Our experts answer your questions with a smile
Monday to Friday 9am - 12.30pm - 2pm - 7pm
01 76 40 35 38
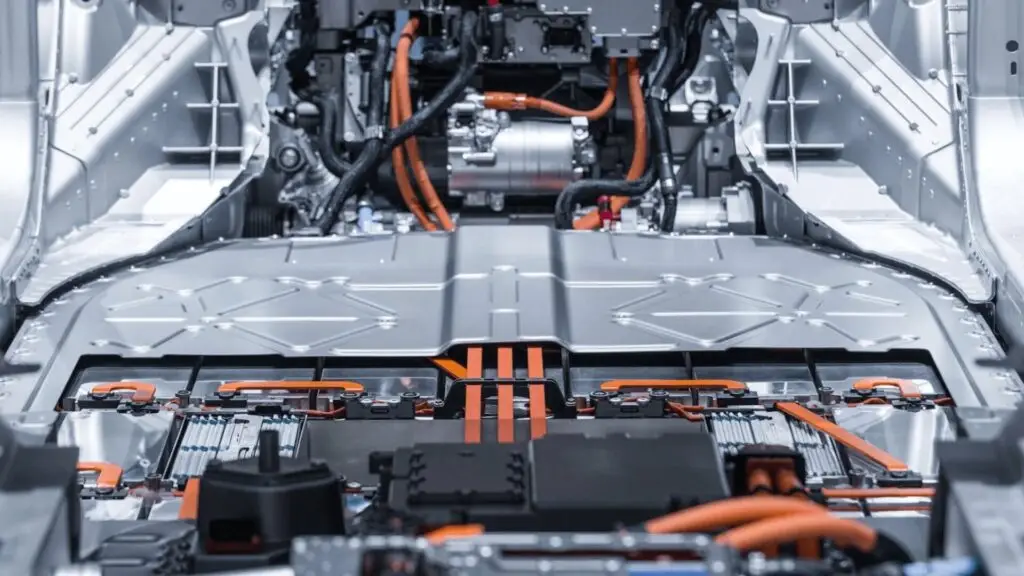
What are the new technologies for electric car batteries?
Electric car batteries have evolved significantly in recent years, with major innovations improving their performance and durability. Here's a look at some of the cutting-edge technologies:
Advanced Lithium-Ion Batteries
Lithium-ion batteries are still the standard for electric vehicles, but they have benefited from a number of improvements:
- Improved Energy Density Modern batteries offer a higher energy density, enabling longer distances to be covered on a single charge. Energy density has increased by 5 to 8 % per year, with recent models reaching 300 Wh/kg. (Beev).
- Thermal Management : More sophisticated thermal management systems extend the life of the battery by maintaining optimum temperatures, thereby reducing heat degradation.
Solid state batteries
Solid electrolyte batteries are a promising development:
- Increased safety They eliminate the risk of fire associated with lithium-ion batteries thanks to the absence of flammable liquid electrolyte.
- Longevity Solid state batteries can withstand more charge/discharge cycles, increasing their lifespan and energy efficiency over the long term.
- Superior capacity These batteries offer an energy density that can exceed 500 Wh/kg, making it possible to considerably increase the energy consumption of the batteries.autonomy vehicles .
Recycling Technologies
New recycling technologies focus on extracting valuable materials more efficiently:
- Materials recovery New methods can recover up to 95 % of materials such as lithium, lead and zinc. cobalt and the nickelreducing the environmental footprint of new battery production.
- Closed loop recycling : Initiatives are underway to reuse recovered materials to make new batteries, thereby promoting a circular economy.
How long does an electric car battery last?
The lifespan of electric car batteries varies according to a number of factors, including technology, conditions of use and thermal management.
Factors Affecting Service Life
- Number of charging cycles Modern lithium-ion batteries can last between 1,500 and 3,000 charge cycles before their capacity starts to diminish significantly, which corresponds to around 10 to 15 years' use for the average driver.
- Temperature Management Effective temperature management minimises the chemical degradation of batteries, extending their life. Liquid cooling systems and battery management software are commonly used to maintain optimum conditions.
Innovations and Progress
- Extended Life Cycle The latest battery technologies promise longer life cycles thanks to improvements in anode and cathode materials that reduce degradation. For example, new silicon batteries can offer up to 5,000 charge/discharge cycles.
- Minimal maintenance Advances in battery management software mean that the health of batteries can be proactively monitored and managed, reducing the need for maintenance and extending their useful life.
Very encouraging customer feedback
Elon Musk, founder of Teslarecently claimed that its batteries would last several hundred thousand kilometres. And we can believe him. Hansjörg Gemmingen is a man with a rather astonishing record: he has covered more than a million kilometres at the wheel of his Tesla Model S in 2013.
The manufacturer NissanFor his part, he is talking about more than 22 years of use before he actually has to change the battery in his electric car. At least, that's what the head of Renault-Nissan Energy Services explained at a conference in Sweden. According to him, the battery life of the Nissan Leaf is 20 to 22 years. In short, this means that the assumed life of a Nissan Leaf battery would be 12 years longer than the life of the car itself.
Adopting eco-responsible driving
It's highly likely that electric cars driving in the hottest climates will lose battery capacity slightly faster than those driving in more temperate regions. Extreme heat is the chemical enemy of lithium-ion, which is why many electric cars are fitted with liquid-cooled batteries.
What's more, older electric cars (the first electric cars on the market) with a relatively short range can deteriorate more quickly. Indeed, driving until the battery is exhausted has a detrimental effect on its lifespan. This is less of a problem these days: with longer ranges, it is very rare to drive until the battery is completely discharged.
To sum up, so as not to shorten the life of your electric caryou need :
- Drive at a normal speed (eco-driving) to extend the life of your battery
- Make small partial charges to avoid overcharging your vehicle
- Ensure that tyres are properly inflated throughout the life of the car
Recycling electric car batteries
The batteries that power electric cars (and even hybrids) can be recycled. For decades, the few electric vehicles on the road were powered by lead-acid batteries. The latest models, lighter and with greater range, use lithium-ion batteries, as do laptops and mobile phones. In both cases, the batteries that power electric cars can be recycled.
In the case of older technology lead-acid batteries, 96 % of the battery materials - including the lead - are recovered. By comparison, only 38 % of the material contained in glass bottles is recovered in the recycling process. They can also be refilled and reused before being recycled.
When the batteries in a lithium-ion vehicle are deemed too worn for driving, they still have up to 80 % of their potential left. So, even before they reach a recycling centre, these batteries are used to support the grid, particularly alongside energy sources that may not be as stable, such as wind or solar power. Batteries can store energy to help the flow of electricity stay on an even keel rather than ebb and flow over time.
As cars with lithium-ion batteries have only just come onto the market, the recycling centres that can recover their components are still in their infancy.
In France, manufacturers have formed a partnership with the SNAM to guarantee the collection, recycling and traceability of batteries in Europe. This network works with several car brands: Peugeot, Citroën, Honda, Volkswagen, Audi, Seat, Skoda, BMW and Toyota.
In 2019, Volkswagen has announced the conversion of its Salzgitter plant to lithium-ion batteries. In practical terms, this means that its site will become a pilot site for opening a battery cell production and recycling line.
READ ALSO - Vehicle-to-grid (V2G): electric cars as a source of energy?
The second life of batteries - second use
This is a second solution for batteries. The idea here is to extend battery life.
Batteries that have become obsolete for a driver's needs can no longer be used in cars. However, they can be used for other applications that require less power from the batteries. This is what is known as the second life of batteries. This process delays battery recycling and reduces the environmental impact of battery production.
Now you know everything about the life of a electric car. If you have any questions, please don't hesitate to contact us at [email protected].
If you would like to find out more aboutsupport for the installation of charging points for private customers in 2024For more information, see our article on this subject.